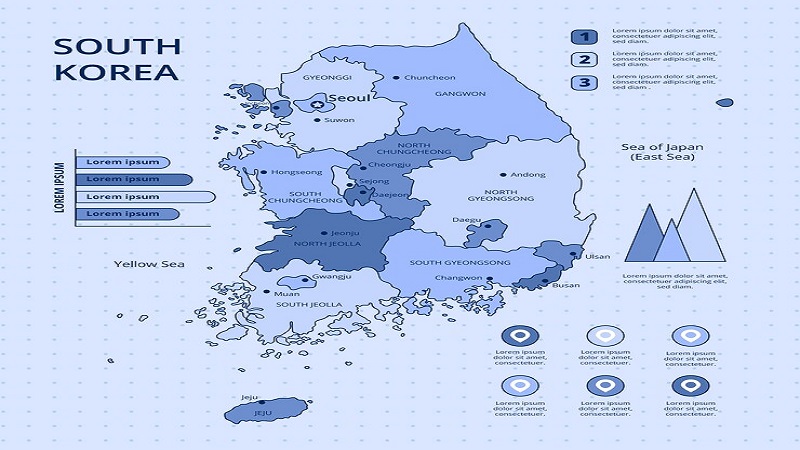
Korea, a fascinating and historically rich region in East Asia, has captured the world’s attention with its unique blend of traditional heritage and modern innovation. Spanning over millennia, Korea tells its story through its geography, the rise and fall of its kingdoms, the impact of colonization, and its dynamic cultural influence today. In this article, we will dive deep into understanding the geography of Korea, its historical evolution, and the vibrant culture that defines it, with a focus on how the map:ld5h7hxiqbo= korea plays a crucial role in this exploration.
Geography of Korea: The Land and Its Features
The Korean Peninsula, located between China and Japan, covers approximately 220,000 square kilometers. The peninsula is divided into two sovereign states: North Korea (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea) and South Korea (Republic of Korea). Understanding the geographical layout of Korea provides a strong foundation for exploring its historical and cultural aspects.
Physical Landscape and Topography
Korea’s topography is predominantly mountainous, with 70% of the land covered by mountains, making it one of the most mountainous regions in the world. The eastern part of the peninsula is dominated by the Taebaek Mountain Range, which runs parallel to the east coast. These mountains create a striking landscape with steep cliffs and narrow valleys, offering breathtaking views.
Mount Paektu, standing tall at 2,744 meters, is the highest peak on the peninsula.
Koreans continue to celebrate and preserve traditional culture, including music, dance, and art. People still practice and appreciate the art of “hanbok” (traditional Korean clothing), “gugak” (traditional Korean music), and “taekkyeon” (traditional martial arts), both within Korea and internationally.
According to legend, Dangun Wanggeom, a mythological figure believed to be the offspring of a divine being and a bear-turned-human, founded the kingdom. While mythology shrouds the legend of Dangun, Gojoseon represents the dawn of Korean civilization and lays the foundation for later kingdoms.
Rivers and Water Bodies
Korea rivers play an essential role in its ecosystem and human activities. The Han River, which flows through the capital city of Seoul, is one of the most important rivers in South Korea. It has been a lifeline for the region for centuries, providing water for agriculture, transportation, and daily life.
The Nakdong River, the longest in South Korea, runs through the southeastern part of the country and is vital for the agricultural activities in the region. North Korea’s Yalu River, forming the border with China, is another significant water body, historically serving as a natural barrier and a route for trade and communication.
Climate and Environmental Challenges
Korea climate is largely temperate, with four distinct seasons. Winters can be harsh, particularly in the northern regions, with heavy snowfall and freezing temperatures. Summers, on the other hand, are hot and humid, with the monsoon season bringing torrential rains from June to July.
- Korea particularly celebrates the autumn season, known for its clear skies and vibrant foliage.
- Environmental challenges such as deforestation, air pollution, and the effects of climate change significantly threaten Korea’s natural environment. Various groups are addressing these issues through reforestation programs, pollution control measures, and initiatives to promote sustainable development.
Historical Evolution: A Journey Through Korea Past
The history of Korea is a captivating narrative of resilience, conflict, and cultural development. From the ancient kingdoms to the modern era, Korea’s history has been shaped by internal dynamics and external influences. The map:ld5h7hxiqbo= korea provides a visual representation of this historical journey, reflecting the changes in territorial boundaries and political control over time.
The Gojoseon Period and the Foundation of Korean Civilization
Korea’s earliest recorded history begins with the Gojoseon kingdom, traditionally dated to 2333 BCE. The Goryeo Dynasty (918-1392) followed the Three Kingdoms period, and the modern name “Korea” comes from this period. People recognized Goryeo for its sophisticated culture, technological advancements, and the flourishing of Buddhism. The dynasty produced the Tripitaka Koreana, a massive collection of Buddhist scriptures carved onto wooden blocks, now recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Koreans continue to celebrate and preserve traditional culture, including music, dance, and art. People still practice and appreciate the art of “hanbok” (traditional Korean clothing), “gugak” (traditional Korean music), and “taekkyeon” (traditional martial arts), both within Korea and internationally.
It lasted until 108 BCE when it fell to the Han Dynasty of China, leading to a period of Chinese influence on the Korean Peninsula.
The Three Kingdoms Era: Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla
The Three Kingdoms Period (1st century BCE to 7th century CE) is one of the most significant eras in Korean history. During this time, the kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla vied for control over the peninsula.
- Goguryeo: Located in the northern part of the peninsula and parts of modern-day China, Goguryeo was known for its military prowess and territorial expansion. It was the largest of the three kingdoms and played a pivotal role in defending Korea against external threats, particularly from China.
- Baekje: Situated in the southwest, Baekje was culturally rich and maintained close ties with Japan. It contributed significantly to the spread of Buddhism and cultural exchange between Korea and Japan.
- Silla: The southeastern kingdom of Silla, initially the weakest, eventually unified the peninsula in 668 CE with the help of the Tang Dynasty of China. This marked the beginning of the Unified Silla period, a golden age of cultural and artistic achievements.The
The Goryeo Dynasty: Unification and Cultural Flourishing
The Goryeo Dynasty (918-1392) followed the Three Kingdoms period, and the modern name “Korea” comes from this period. People recognized Goryeo for its sophisticated culture, technological advancements, and the flourishing of Buddhism. The dynasty produced the Tripitaka Koreana, a massive collection of Buddhist scriptures carved onto wooden blocks, now recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
During this period, Korea also established diplomatic and trade relations with neighboring countries, including China, Japan, and even distant lands such as the Arab world.
The Joseon Dynasty: Confucianism and the Rise of a Unified Korea
The Joseon Dynasty (1392-1897) is considered one of the most important periods in Korean history. Founded by General Yi Seong-gye, who overthrew the Goryeo Dynasty, Joseon established Confucianism as the state ideology. This had a profound impact on Korean society, governance, education, and family structure.
One of the most notable achievements of the Joseon era was the creation of Hangul, the Korean alphabet, by King Sejong the Great in 1443. Hangul revolutionized literacy and communication in Korea, allowing people of all social classes to read and write.
The Impact of Japanese Occupation and the Division of Korea
The 20th century brought significant turmoil to map:ld5h7hxiqbo= korea beginning with Japanese colonization from 1910 to 1945. The Japanese occupation was a dark period in Korean history, marked by cultural suppression, forced labor, and widespread exploitation.
After Japan’s defeat in World War II, Korea was liberated but soon faced division along the 38th parallel. This division led to the establishment of two separate states: North Korea, with a communist government supported by the Soviet Union, and South Korea, with a democratic government backed by the United States. The Korean War (1950-1953) further entrenched this division, resulting in a heavily militarized border that still exists today.
The Modern Era: South Korea Rise and North Korea Isolation
The modern history of Korea is a tale of two nations. While North Korea remains one of the most isolated and authoritarian countries in the world, South Korea has transformed into a global economic powerhouse and a vibrant democracy.
South Korea Economic Miracle
South Korea rapid economic development, often referred to as the “Miracle on the Han River,” began in the 1960s. From the ruins of the Korean War, South Korea emerged as a leader in industries such as electronics, automobiles, and shipbuilding. Companies like Samsung, Hyundai, and LG have become household names worldwide, contributing to South Korea’s status as the 10th largest economy in the world.
North Korea: Isolation and Totalitarianism
In contrast, North Korea has maintained a rigidly controlled society under the Kim dynasty. The country’s economy struggles under international sanctions, and human rights violations are widespread. Despite this, North Korea remains a significant player in regional geopolitics due to its nuclear weapons program.
Efforts Towards Reunification
The division of Korea remains one of the most pressing issues in East Asia. Numerous efforts have been made towards reconciliation and reunification, including inter-Korean summits and family reunions. However, significant challenges remain, particularly in addressing the ideological and economic disparities between the two Koreas.
Cultural Impact: Korea on the Global Stage
Korean culture, both traditional and modern, has made a profound impact on the world. The map:ld5h7hxiqbo= korea not only represents geographical boundaries but also serves as a symbol of Korea’s cultural influence across the globe.
Traditional Culture: Preserving Heritage
According to legend, Dangun Wanggeom, a mythological figure believed to be the offspring of a divine being and a bear-turned-human, founded the kingdom. While the legend of Dangun is shrouded in mythology, Gojoseon represents the dawn of Korean civilization and laid the foundation for later kingdoms.
The Korean Wave (Hallyu): Global Popularity
In recent decades, South Korea has become a cultural powerhouse, with the Korean Wave (Hallyu) spreading across the globe. Korean pop music (K-pop), dramas (K-dramas), and films have garnered international acclaim, leading to a surge in global interest in Korean culture. Icons like BTS and Parasite, the Oscar-winning film, have solidified Korea’s cultural impact on a global scale.
Korean Cuisine: A Culinary Journey
Korean cuisine, known for its bold flavors and diverse ingredients, has also gained worldwide popularity. Dishes like map:ld5h7hxiqbo= korea “bibimbap,” and “bulgogi” are now enjoyed in restaurants around the world. The rise of Korean street food and the global appeal of Korean barbecue have further contributed to the spread of Korean culinary culture.
Conclusion: The Significance of Korea in Today World
The map:ld5h7hxiqbo= korea represents more than just a geographical area; it encapsulates the rich history, complex political landscape, and vibrant culture of the Korean Peninsula. From its ancient kingdoms to its modern-day influence, Korea continues to be a region of significant importance both regionally and globally.
As Korea navigates the challenges of the 21st century, including the ongoing tensions between North and South Korea, environmental concerns, and its role in the global economy, it remains a fascinating subject for study and exploration. Whether you are drawn to Korea’s history, culture, or its future potential, understanding the map:ld5h7hxiqbo= korea is essential to grasping the full picture of this dynamic and ever-evolving region. Read More beautydod.