Guatemala, a country rich in history, culture, and natural beauty, is a fascinating place to explore both physically and geographically. The landscape, which includes mountains, rainforests, lakes, and ancient ruins, creates a tapestry that captures the attention of travelers, researchers, and locals alike. By understanding the various aspects of Guatemala’s geography through maps, we can better appreciate the complexities and treasures that the country holds. This article will explore the meaning of map:te9vcjtdaa8= guatemala while diving into the country’s physical features, cultural landmarks, and the evolving role of mapping technologies.
Decoding the Title: What Does Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala Mean?
The term map:te9vcjtdaa8= guatemala appears to be a unique reference that may be associated with a specific mapping platform or digital map identifier for Guatemala. Although it does not correspond to a widely recognized geographic term, it serves as a prompt to explore the use of maps in understanding Guatemala’s diverse landscapes and how digital technologies have revolutionized the way we interact with geographic data.
An Overview of Guatemala Geography
Location and Borders
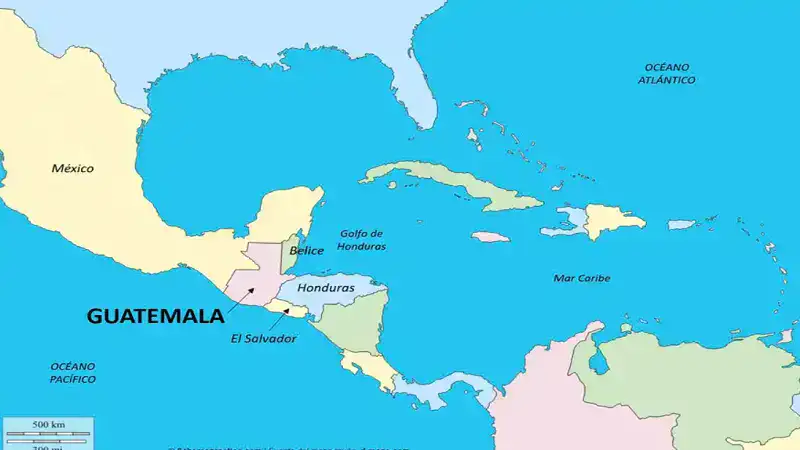
Guatemala is located in the northern part of Central America, sharing borders with Mexico to the north and west, Belize to the northeast, Honduras to the east, and El Salvador to the southeast. The southern edge of the country faces the Pacific Ocean, while the northeastern side touches the Caribbean Sea. This strategic position provides the country with access to various trade routes and influences cultural exchanges across the region.
Significance of Guatemala Position in Central America
Being situated between North and South America, Guatemala serves as a bridge for migratory species, trade, and cultural exchange. Its geographical location also makes it prone to natural disasters such as earthquakes and hurricanes, which have shaped the nation’s development and resilience.
Guatemala Topography: Mountains, Valleys, and Volcanoes
Mountain Ranges and Peaks
The Sierra Madre mountain range runs across much of Guatemala, characterized by steep, rugged terrain and elevations that often exceed 3,000 meters. The country’s topography is also punctuated by numerous valleys that support agriculture and human settlement.
Volcanoes and Their Influence on the Land
Guatemala is home to more than 30 volcanoes, with some of the most famous being Volcán de Fuego, Pacaya, and Acatenango. These volcanoes not only define the landscape but also impact the local agriculture through volcanic ash, which enriches the soil. However, active volcanoes pose risks of eruptions and earthquakes.
Rivers and Lakes: Guatemala Lifelines
The Role of Major Rivers in Transportation and Agriculture
Rivers such as the Motagua, Usumacinta, and Polochic play critical roles in transportation, agriculture, and power generation. They provide irrigation for farmlands, support hydroelectric plants, and act as natural borders in some regions.
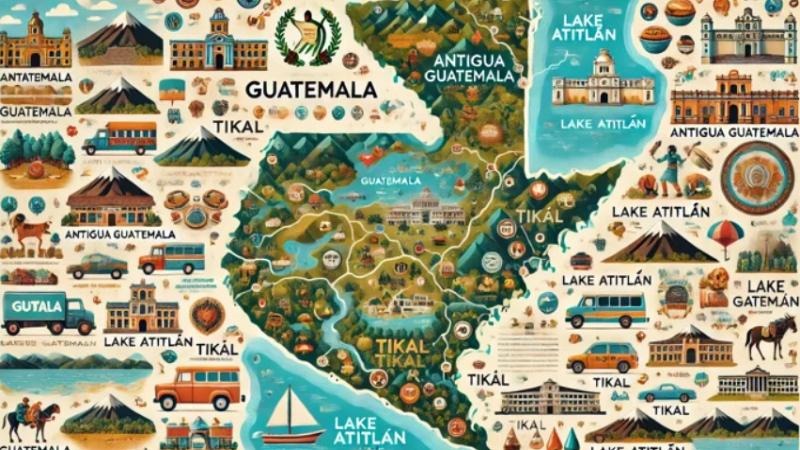
The Cultural and Ecological Importance of Lake Atitlán
Lake Atitlán, surrounded by volcanoes and traditional Mayan villages, is not only a natural wonder but also a cultural symbol. It is considered one of the most beautiful lakes in the world, attracting tourists and fostering local traditions. The lake’s ecology is closely monitored to prevent pollution and preserve its biodiversity.
Exploring Guatemala Rainforests and Biodiversity
Diversity of Flora and Fauna
Guatemala’s rainforests are among the richest in biodiversity within Central America, hosting countless species of plants and animals. The Petén region is particularly notable for its dense forests, which are home to species like the jaguar, ocelot, and howler monkey.
Threats to Wildlife and Conservation Efforts
Deforestation and habitat fragmentation pose significant threats to map:te9vcjtdaa8= guatemala wildlife. Efforts by local and international organizations focus on creating protected areas, restoring degraded lands, and promoting sustainable development to combat these issues.
Climate Zones of Guatemala: A Land of Contrasts
Highlands: The Cool and Temperate Climate
The highlands, including areas such as Quetzaltenango and Antigua, experience a cooler, more temperate climate due to their elevation. These regions are suitable for growing coffee, potatoes, and other crops that thrive in cooler temperatures.
Lowlands and Coastal Areas: Tropical Heat and Rainfall
In contrast, the lowlands and coastal regions, including areas along the Pacific and Caribbean coasts, experience a tropical climate with high temperatures and substantial rainfall. These areas are characterized by lush vegetation and support crops like bananas, sugarcane, and cocoa.
Guatemala Cultural and Historical Landmarks
Ancient Mayan Sites: Tikal and Beyond
Guatemala is home to some of the most impressive Mayan archaeological sites, including Tikal, which was once one of the most powerful cities in the ancient Maya civilization. Other notable sites include Yaxhá, El Mirador, and Uaxactún, each offering a glimpse into the rich history and architectural achievements of the Maya.
Colonial Architecture and Its Significance
In addition to its ancient ruins, Guatemala also features beautiful colonial architecture, particularly in cities like Antigua. This historic city is renowned for its well-preserved Spanish Baroque buildings and cobblestone streets, which draw visitors seeking a taste of the country’s colonial past.
How Geography Shapes Guatemala Economy
The Agricultural Landscape
Guatemala’s economy relies heavily on agriculture, with coffee, bananas, and sugar among its leading exports. The varied geography allows for different types of crops to be cultivated, depending on the altitude, soil type, and climate.
Tourism and Its Dependence on Natural Geography
Tourism is another vital sector, supported by the country’s natural beauty, historical sites, and diverse ecosystems. Adventure tourism, including activities such as hiking, caving, and birdwatching, is particularly popular, drawing nature enthusiasts from around the world.
The Evolution of Mapping in Guatemala
Traditional Cartography vs. Modern GIS
Mapping in Guatemala has evolved from traditional hand-drawn maps to modern Geographic Information Systems (GIS) that offer digital mapping and spatial analysis. GIS technologies have made it easier to map remote areas, analyze environmental changes, and plan infrastructure projects.
Mapping Challenges in Remote Areas
Remote regions, such as those deep in the rainforest, pose challenges due to limited access and dense vegetation. However, modern technology like LiDAR and drones has improved the accuracy and efficiency of mapping these areas.
Technological Advances in Mapping and Navigation
Using Digital Maps for Daily Life and Travel
Digital maps, powered by GPS and satellite imagery, have become indispensable tools for navigation, especially for travelers exploring Guatemala’s diverse landscapes. Apps like Google Maps and specialized hiking apps help visitors find their way even in remote locations.
Impact of GPS and Satellite Imagery on Navigation
The availability of GPS and satellite imagery has greatly improved the accuracy of maps and the ability to track changes in the environment. This technology supports emergency response during natural disasters and guides development projects.
Mapping for Conservation and Environmental Protection
How Mapping Helps in Conservation Planning
Maps are essential in identifying conservation priorities, such as areas that need protection or restoration. They also help track deforestation rates and monitor wildlife populations.
Efforts to Track and Combat Deforestation
Using satellite data, conservation organizations can detect illegal logging and other activities that threaten the rainforest, allowing for timely interventions to protect these areas.
Using Maps for Adventure Travel in Guatemala
Popular Hiking and Trekking Routes
Guatemala offers numerous trekking opportunities, such as hiking to the summit of Acatenango or exploring the trails around Lake Atitlán. Accurate maps ensure that hikers can safely navigate these routes.
Navigating Guatemala Off-the-Beaten-Path Destinations
For travelers looking to venture off the tourist trail, maps are crucial for exploring lesser-known places like the Cuchumatanes mountain range or the Rio Dulce. These areas provide unique experiences for those willing to seek out the less accessible corners of the country.
The Future of Mapping in Guatemala
Innovations on the Horizon
The future of mapping in Guatemala will likely include increased use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies, which can provide immersive experiences for users, whether for education, tourism, or urban planning.
The Potential for Enhanced Virtual and Augmented Reality Maps
Virtual and augmented reality maps could transform the way people interact with geographic data, allowing users to experience locations in an immersive 3D environment, which could also be used to promote virtual tourism.
Conclusion
Maps are more than just tools for navigation; they are gateways to understanding a country’s geography, culture, and history. In Guatemala, mapping reveals a story of diverse landscapes, ancient civilizations, and ongoing efforts to balance development with conservation. Exploring map:te9vcjtdaa8= guatemala offers insights into this fascinating nation, inviting travelers and researchers alike to discover its hidden gems. Read More beautydod.
FAQs
-
What does Map:te9vcjtdaa8= Guatemala refer to?
It likely represents a digital mapping reference or code used in specific applications to identify the geographical data related to Guatemala.
-
Why is Guatemala known for its biodiversity?
Guatemala varied climate zones and topography support a rich diversity of ecosystems, from rainforests to highland plateaus, which harbor numerous plant and animal species.
-
How do maps help in conservation efforts?
Maps enable the monitoring of deforestation, guide the establishment of protected areas, and assist in tracking wildlife populations for effective conservation planning.
-
What are some must-visit natural landmarks in Guatemala?
Lake Atitlán, the volcanoes of the Sierra Madre, and the Mayan ruins of Tikal are among the top attractions that showcase Guatemala’s natural beauty and historical significance.
-
How has modern technology changed mapping in Guatemala?
The use of GPS, satellite imagery, and GIS technologies has improved mapping accuracy, disaster response capabilities, and urban planning across the country.